Breathing Techniques for Stress Relief: Ultimate Guide
Learn evidence-based breathing techniques for stress relief, better sleep, and calmer focus. Compare methods, timing, and a 14-day plan you can start tonight.
11 Min Read
Why Breathing Can Change Stress Fast
When stress hits, your body does not wait for your opinion. Heart rate climbs, muscles tighten, and your breathing often gets shallow and fast. That pattern makes sense during real danger. It is less helpful when the "threat" is an unread inbox, a hard conversation, or lying awake at 2 a.m.
The useful part is this: breathing is one of the few automatic body systems you can also control on purpose. A slow, deliberate breath can act like a direct signal to your nervous system that says, "We are safe enough to downshift." Organizations like the American Heart Association include structured breathing in practical stress-management guidance for exactly this reason.
If you have been feeling chronically wired, you are not imagining the wear-and-tear. We cover that broader biology in our guide on how chronic stress disrupts hormones and recovery. Breathing drills are not a complete cure for long-term overload, but they are one of the fastest tools you can use between appointments, workouts, and sleep routines.
Short version: one good breathing cycle may not fix your life, but it can interrupt the stress spiral long enough for better decisions to come back online.
In this guide, you will get a realistic framework: what the evidence says, where breathing helps most, how to choose techniques based on symptoms, and how to build a 14-day plan that fits normal life instead of a perfect schedule.

The Science: Slow Breathing and Your Nervous System
Controlled breathing changes more than mood. It can alter measurable physiology in the moment and over time. A large meta-analysis on voluntary slow breathing found consistent increases in vagally mediated heart rate variability, both during sessions and after repeated practice, which supports the idea that paced breathing can strengthen parasympathetic activity in many contexts (PubMed: 35623448).
That does not mean every breathing pattern works equally well for every person. It does mean your practice can be strategic: if stress is high, lower your breathing rate and lengthen exhale; if focus is low, use slightly more alert patterns without over-breathing. A systematic review focused on diaphragmatic breathing found improvements in stress biomarkers and self-reported stress across included adult studies (PubMed: 31436595).
Mechanistically, breath influences your autonomic state through multiple pathways, including baroreflex effects, respiratory sinus arrhythmia, and vagal signaling. One experimental study on paced yogic breathing showed low-frequency HRV changes were largely vagally mediated under those conditions (PubMed: 29771730). Translation: the pattern of your breath can materially shift how "amped" your nervous system feels.
There is also emerging clinical relevance for sleep and stress loops. In a controlled insomnia study, slow paced breathing increased autonomic markers associated with calm and improved sleep quality metrics (PubMed: 25234581). If nights are your worst window, this is especially worth testing.
Breathing is still one tool, not a replacement for therapy, medication, trauma-informed care, or medical treatment. But the evidence base is strong enough to treat it as a core self-regulation skill instead of a vague wellness add-on.
What breathing can do quickly
- Reduce the intensity of a stress surge within 1-3 minutes.
- Lower felt anxiety before meetings, travel, public speaking, or bedtime.
- Improve body awareness so you catch tension earlier.
- Support sleep onset when rumination is the main barrier.
What breathing cannot do alone
- Resolve severe insomnia with major medical or psychiatric drivers.
- Treat panic disorder or PTSD without broader care.
- Replace blood-pressure medications or cardiology follow-up.
- Compensate for chronic sleep deprivation forever.
| Claim | Evidence strength | Practical interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Slow breathing can improve parasympathetic markers (HRV) | Moderate to strong (large meta-analysis) | Useful for stress downshifting and autonomic balance practice |
| Diaphragmatic breathing can reduce stress outcomes | Moderate (systematic review with smaller studies) | Good first technique for daily use and beginner training |
| Paced breathing can support sleep quality in some adults | Moderate (small controlled studies) | Best used as part of a wind-down routine, not as a solo cure |
How to Check Your Baseline Before You Start
Most people skip this and then wonder if a method "works." Start with a two-minute baseline check:
- Sit down with both feet on the floor, shoulders loose, jaw unclenched.
- Set a timer for 60 seconds and count breaths (one inhale + one exhale = one breath).
- Rate stress 0-10, where 0 is calm and 10 is max overload.
- Notice where breath is happening: upper chest, belly, or both.
Repeat the same check after a breathing set. If your breath rate drops and stress score moves down even one or two points, you have objective feedback. You do not need perfection; you need measurable direction.
This is also where pattern recognition starts. Many people who feel "mentally anxious" are actually running a subtle over-breathing pattern all day. If this sounds familiar, compare your symptoms with our clinical deep dive on anxiety, burnout, and biological stress load. The overlap is bigger than most people expect.
Quick readiness checklist
- Can you breathe through your nose comfortably most of the time?
- Do you feel dizzy when you try deep breathing? If yes, slow down and reduce volume.
- Do you hold your breath while checking messages or working?
- Is sleep initiation harder than staying asleep?
Your answers help you pick techniques that fit your real bottleneck rather than copying random routines from social media.
Best Breathing Techniques and When to Use Each
Not every technique is built for the same moment. Some are best for acute stress spikes, others for bedtime, and others for daytime resilience training. Use the table first, then the step-by-step instructions below.
| Technique | Pattern | Best use case | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physiological sigh | Two short inhales, one long exhale | Immediate stress spikes | 1-3 minutes |
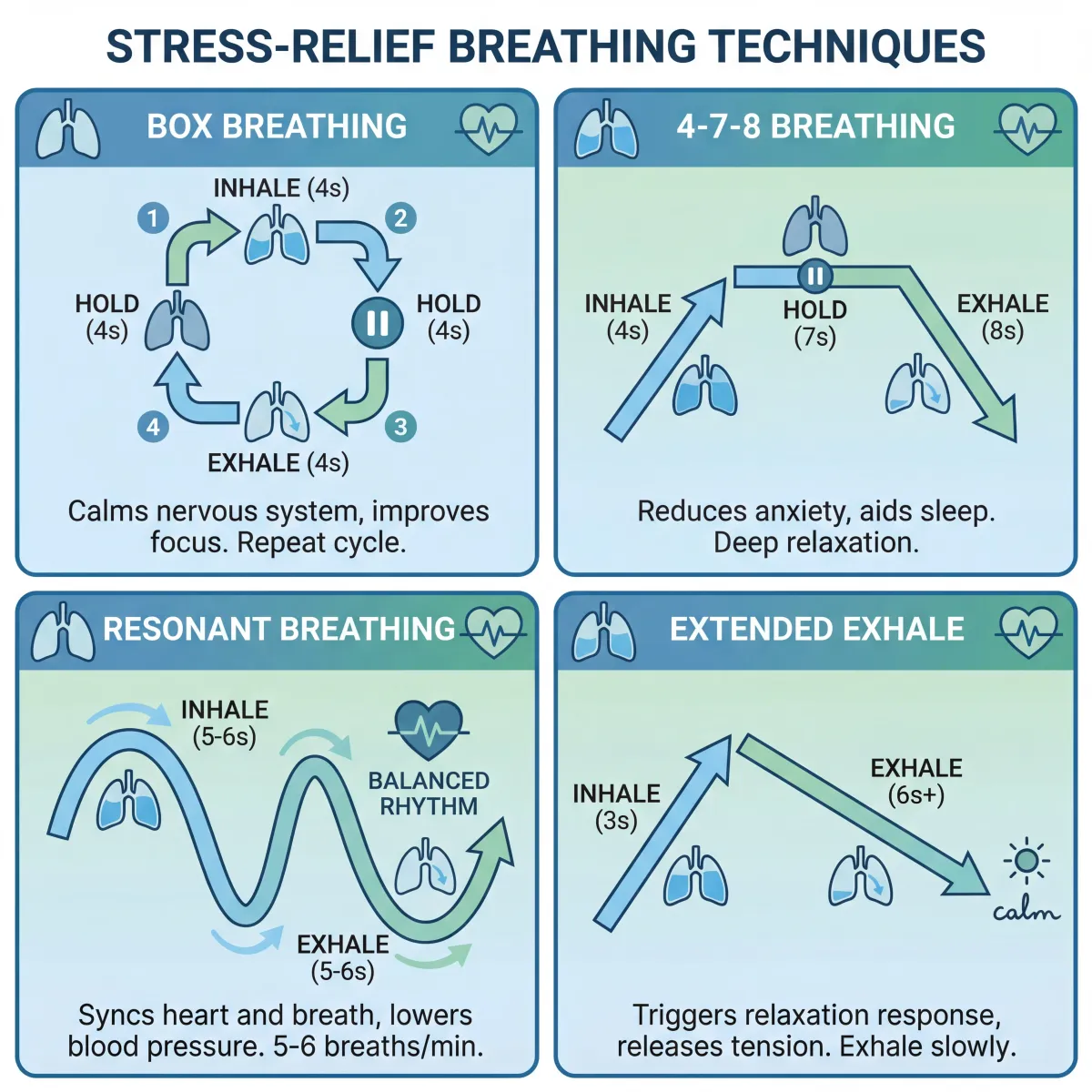
| Box breathing | Inhale 4, hold 4, exhale 4, hold 4 | Pre-performance calm focus | 3-5 minutes |
| 4-7-8 breathing | Inhale 4, hold 7, exhale 8 | Evening decompression | 2-4 cycles to start |
| Resonant breathing | About 5-6 breaths/minute | Daily autonomic training | 10 minutes |
| Diaphragmatic breathing | Belly expands on inhale, slow exhale | General stress reduction | 5-10 minutes |
1) Physiological sigh for immediate de-escalation
Do a short inhale through the nose, then another shorter inhale without exhaling, then a long relaxed exhale through the mouth. Repeat for 1-2 minutes. Keep effort low. This is the fastest "break-glass" drill when agitation suddenly rises.
Use it before difficult calls, during commute stress, or when you notice the first signs of escalation. If your body is stuck in fast chest breathing, this pattern helps unload air and lowers urgency quickly.
2) Box breathing for controlled calm and focus
Inhale for four counts, hold for four, exhale for four, hold for four. Repeat 8-12 rounds. Keep shoulders down and jaw soft. If four-count holds feel uncomfortable, start with 3-3-3-3 and build up.
Box breathing works well for transitions: before presentations, before entering family conflict, or before exercise if your mind is racing. It is simple enough to remember under pressure and structured enough to prevent over-breathing.
3) 4-7-8 breathing for bedtime downshift
Inhale through the nose for four counts, hold for seven, then exhale slowly for eight. Start with two to four cycles. Do not force giant inhales. The goal is rhythm, not lung-maxing.
The longer exhale is often the key lever for switching from alert mode toward sleep mode. If sleep onset is a recurring issue, pair this with a low-light routine and reduced screen exposure. You can also combine this with the sleep hygiene framework in our guide to sleep disorders, causes, and treatment strategies.
4) Resonant breathing for daily nervous-system training
Set a pacer at roughly 5-6 breaths per minute. A simple starting rhythm is inhale 5 seconds, exhale 5 seconds. Do this for 10 minutes once or twice daily. Over time, many people find this gives them a calmer baseline between stressful events, not just during them.
This method aligns closely with research on slow breathing and autonomic regulation (PubMed: 35623448). Think of it like skill training, similar to mobility work for your stress system.
5) Diaphragmatic breathing for stress, mood, and body awareness
Place one hand on the upper chest and one on the abdomen. Inhale through the nose and let the lower hand rise first. Exhale slowly, slightly longer than inhale. Repeat for 5-10 minutes. A trial in healthy adults found improvements in stress-related outcomes including cortisol and negative affect after training (PubMed: 28626434).
If you only commit to one method this week, make it this one. It transfers well to meetings, traffic, bedtime, and early-morning anxiety.

How to pick the right technique by symptom
| What you feel right now | Likely breathing problem | Best first technique | Backup option |
|---|---|---|---|
| Racing thoughts, heart pounding | Fast shallow breathing | Physiological sigh | Box breathing |
| Tension before sleep | High evening arousal | 4-7-8 breathing | Resonant breathing |
| Afternoon burnout and irritability | Stress accumulation | Diaphragmatic breathing | Resonant breathing |
| Pre-event jitters with poor focus | Overactivation + cognitive noise | Box breathing | Diaphragmatic breathing |
Common Mistakes That Cancel the Benefits
You can "do breathing" and still miss most benefits. Here are the errors I see most often.
Breathing too big instead of too calm
People hear "deep breathing" and try to inhale to full capacity every time. That can create lightheadedness and chest tension. In most stress protocols, you want slower and smoother, not maximal volume.
Overusing breath holds
Holds can be useful, but long holds are not mandatory and can backfire if you are already anxious. If holds increase urgency, shorten them or remove them temporarily. Exhale length is often enough.
Practicing only when overwhelmed
Emergency use matters, but daily low-stress practice is what builds resilience. Training when calm improves your odds of using the skill when it matters most.
Ignoring posture and jaw tension
If shoulders are elevated and jaw is clenched, breathing mechanics suffer. Relaxing these areas can improve effectiveness immediately.
Expecting breathing to solve root causes by itself
If stress load comes from chronic sleep debt, untreated anxiety, trauma, alcohol use, or pain, breathing should sit inside a larger plan. It is a powerful lever, not the whole machine. For broader mind-body routines, our article on meditation techniques and stress recovery can help you build that stack.
A 14-Day Breathing Plan for Real-Life Stress
This plan is intentionally simple. You are building consistency, not collecting fancy protocols.
| Day range | Morning | Midday reset | Evening | Goal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days 1-3 | 5 min diaphragmatic breathing | 1 min physiological sigh | 2 cycles 4-7-8 | Learn mechanics and reduce over-breathing |
| Days 4-7 | 8 min resonant breathing | 3 min box breathing | 4 cycles 4-7-8 | Build rhythm and stress interruption skill |
| Days 8-11 | 10 min resonant breathing | 1-2 min physiological sigh as needed | 6 min diaphragmatic breathing | Improve baseline calm and sleep entry |
| Days 12-14 | 10 min preferred method | 3 min box or diaphragmatic before stressor | 4-6 cycles 4-7-8 | Personalize your long-term routine |
How to track progress without overcomplicating it
- Breath rate before and after one session each day.
- Stress score (0-10) before and after.
- Sleep latency estimate (how many minutes to fall asleep).
- Whether you used a technique during an actual stress moment.
By day 14, many people report fewer "all-or-nothing" stress surges and better recovery after triggers. If that does not happen, do not conclude breathing is useless. It may mean pattern mismatch, too much breath-holding, or unresolved drivers that need clinical support.
Who Should Use Caution or Get Medical Advice First
Breathing practices are generally low risk, but caution is appropriate in some cases:
- Uncontrolled asthma, COPD, or significant chronic lung disease.
- Recent cardiac events or unstable cardiovascular symptoms.
- Frequent dizziness, fainting, or unexplained chest pain.
- Panic symptoms that worsen with interoceptive focus.
- Trauma histories where inward focus feels destabilizing.
If you have a condition in those categories, discuss technique selection with your clinician first. You can often still practice, but dosage and style should be individualized.
For people with insomnia, anxiety, or blood pressure concerns, breathing is most effective when combined with standard care, movement, sleep hygiene, and therapy when indicated. The NCCIH overview on meditation and mindfulness offers a balanced perspective on benefits and limitations, including safety considerations.
If your stress pattern is strongly tied to cognitive and mood symptoms, pairing breath work with movement-based mind-body practice can help. Our guide on brain and mood benefits of yoga is a practical next step for that combination approach.

Frequently Asked Questions
How long does breathing practice take to reduce stress?
Acute stress can drop within 1-3 minutes if you use the right pattern, especially longer exhales. Baseline resilience usually takes 2-6 weeks of regular practice.
What is the best breathing technique for anxiety at night?
Most people do well with 4-7-8 or gentle diaphragmatic breathing with extended exhale. Keep the pace comfortable and avoid forceful inhales that can increase arousal.
Can breathing exercises lower blood pressure?
They may help as part of a broader plan, particularly slow diaphragmatic or paced breathing routines. They should not replace prescribed blood pressure treatment without clinician guidance.
Why do I feel dizzy when I try deep breathing?
Dizziness usually comes from over-breathing, not under-breathing. Reduce breath size, slow the pace, and prioritize smooth exhales through the nose or gently through pursed lips.
Should I breathe through my nose or mouth for stress relief?
Nasal breathing is generally preferred for most stress drills because it promotes slower, more controlled airflow. Mouth exhale can be useful in specific techniques like physiological sigh or 4-7-8.
Final Takeaway
Breathing is not a miracle shortcut. It is better than that: a reliable, repeatable skill that gives you control during moments when stress would otherwise run the show. Start with one method, practice daily for two weeks, and use objective check-ins. If symptoms remain intense, keep breathing as a support tool while you address larger drivers with professional care.
If you want one rule to remember, use this: when stress rises, slow the breath and lengthen the exhale. It is a small action with surprisingly high leverage.
Related Articles
- The Hidden Toll of Low-Level Stress - Learn how chronic stress alters cortisol rhythms, sleep, and recovery capacity.
- The Real Damage Anxiety and Burnout Do to Your Body - A clinical look at inflammation, mood, and systemic effects of prolonged anxiety load.
- Sleep Disorders: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Guide - Use this guide when stress and poor sleep start feeding into each other.
- Meditation Techniques, Guides, Tips and Benefits - Pair breathing with simple mindfulness methods for more durable stress control.
- Yoga for a Healthy Mind - Add movement and breath coordination to improve mood regulation and focus.
Medical Disclaimer
This article is for informational and educational purposes only and is not medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a licensed physician or qualified healthcare professional regarding any medical concerns. Never ignore professional medical advice or delay seeking care because of something you read on this site. If you think you have a medical emergency, call 911 immediately.